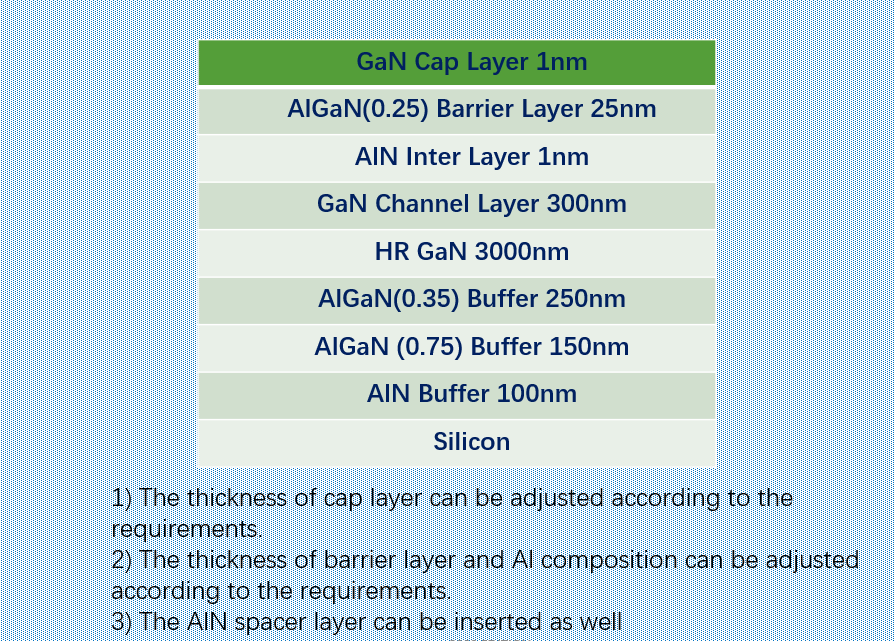
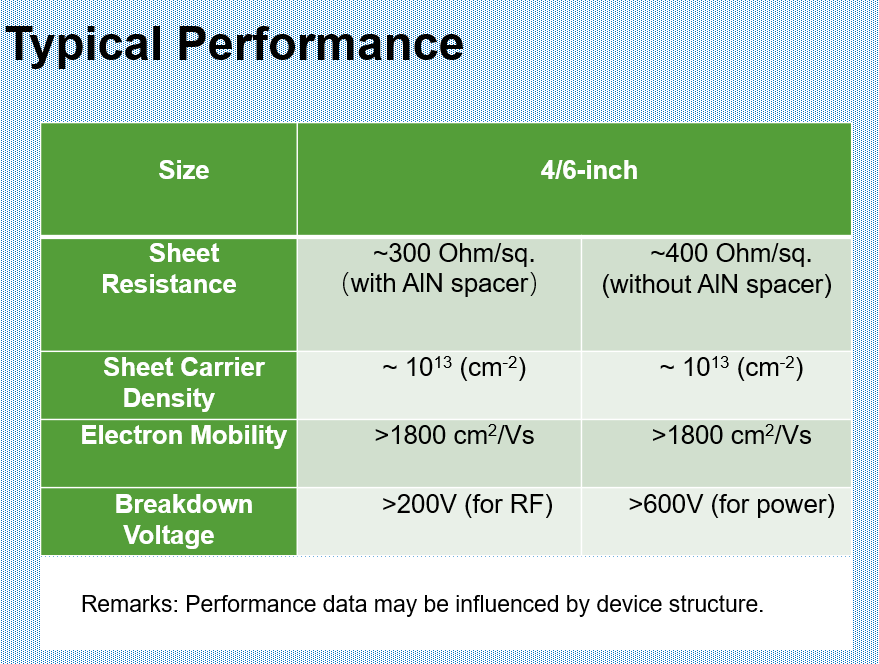
Gallium nitride (GaN) high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) offer an alternative in place of MOSFETs and IGBTs for high-voltage and high-frequency motor-drive applications. These wide band-gap semiconductor devices are opening up new applications for high-power density motors because they are able to handle higher voltages, currents, temperatures, and switching frequencies with much lower losses than silicon transistors. The commercial availability of integrated GaN HEMTs and driver inverter stages for high-power-density electric motor applications is easing the adoption of the new technology.